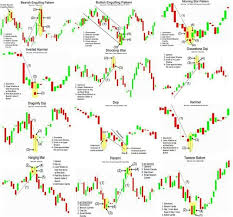
Trading financial markets—whether stocks, forex, cryptocurrencies, or commodities—can be both rewarding and risky. Success in trading requires more than luck; it demands a solid strategy backed by discipline, analysis, and emotional control. This article explores the most effective trading strategies, breaks down how they work, and offers tips to help you choose the right one based on your goals and trading style.
1. What Is a Trading Strategy?
A trading strategy is a fixed plan designed to achieve profitable returns by going long or short in markets. It involves rules for entering and exiting trades, managing risk, and allocating capital. A well-defined strategy removes emotion from the decision-making process and provides a structured approach to trading.
2. Categories of Trading Strategies
Trading strategies generally fall into two categories: technical and fundamental. Most traders use a blend of both.
- Technical trading relies on price charts, indicators, and patterns.
- Fundamental trading focuses on macroeconomic data, financial statements, and news.
Let’s explore the most popular and proven strategies.
3. Day Trading
Day trading involves buying and selling financial instruments within the same day, often holding positions for minutes or hours.
Key Characteristics:
- High frequency of trades
- Uses technical analysis
- Seeks to profit from short-term price movements
Tools Used:
- Moving Averages
- MACD
- RSI
- Volume analysis
Pros:
- Quick gains
- No overnight risk
Cons:
- High stress
- Requires constant monitoring
Day trading is suited for experienced traders with the ability to make fast decisions and handle volatility.
4. Swing Trading
Swing trading aims to capture “swings” in price over days or weeks.
Key Features:
- Longer holding periods than day trading
- Focuses on trend reversals or continuation patterns
Common Strategies:
- Moving average crossovers
- Fibonacci retracements
- Bollinger Bands
Pros:
- Less time-intensive than day trading
- Captures larger price moves
Cons:
- Exposure to overnight risk
- Requires patience and strong market analysis skills
Swing trading is ideal for traders with full-time jobs who can analyze the markets in the evenings or on weekends.
5. Scalping
Scalping is an ultra-short-term strategy that involves making dozens or hundreds of trades per day to capture small profits.
Tools & Indicators:
- 1-minute or 5-minute charts
- Order flow analysis
- High-frequency trading bots (in advanced cases)
Pros:
- Many trading opportunities
- Minimizes exposure to large market moves
Cons:
- Requires extreme focus
- High transaction costs
Scalping is suitable for those who thrive in fast-paced environments and can execute trades quickly.
6. Trend Following
Trend following strategies involve identifying the direction of market movement and trading in that direction.
Techniques:
- Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD)
- Trendlines
- Average Directional Index (ADX)
Example:
If the 50-day moving average is above the 200-day moving average, and price is trending upward, a trader may enter a long position.
Pros:
- Simple to understand
- Works well in strong markets
Cons:
- Doesn’t work well in sideways or choppy markets
- Prone to whipsawing
Trend following is great for traders who like to go with the flow and avoid guessing reversals.
7. Counter-Trend (Mean Reversion) Trading
This strategy bets on the reversal of a current trend, assuming that price will revert to its mean (average).
Tools:
- RSI (Relative Strength Index)
- Bollinger Bands
- Stochastic Oscillator
Strategy Example:
If RSI exceeds 70 (overbought), a counter-trend trader may short the asset expecting a correction.
Pros:
- Good for range-bound markets
- High reward-to-risk ratios
Cons:
- Risky in strong trending markets
- Requires strict stop-loss management
Mean reversion works well for disciplined traders who rely on statistical probabilities.
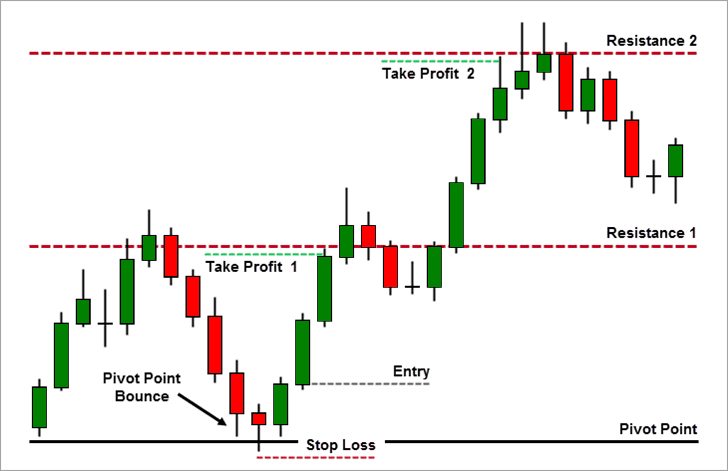
8. Breakout Trading
Breakout strategies involve entering a trade when the price moves outside of a defined support/resistance level.
Indicators:
- Volume spikes
- Price action patterns like triangles or rectangles
- Pivot points
Example:
A breakout above a resistance level with high volume is a signal to enter a long position.
Pros:
- Early entry into new trends
- High momentum trades
Cons:
- High number of false breakouts
- Can result in stop-loss hunting
Breakout trading suits traders who are comfortable with volatility and can react quickly.
9. News-Based Trading
This strategy relies on trading around economic data releases and breaking news.
Events to Watch:
- Interest rate decisions
- Earnings reports
- Jobs reports
- Geopolitical developments
Pros:
- High volatility = potential for large profits
- Suitable for short-term trades
Cons:
- High risk
- Slippage and spread widening are common
News trading is best for those who stay up-to-date with current events and can handle unpredictable market reactions.
10. Algorithmic and Quantitative Strategies
These are automated strategies developed using programming and statistical models.
Tools Used:
- Python, R, or trading platforms with scripting support (like MetaTrader)
- Backtesting software
- Machine learning models
Types:
- Arbitrage
- Statistical arbitrage
- High-frequency trading (HFT)
Pros:
- Emotionless, consistent execution
- Backtestable
Cons:
- Requires technical skills
- Can malfunction if not properly coded
Algorithmic trading is ideal for programmers or those working with technical teams.
11. Risk Management in Trading Strategies
Even the best trading strategy can fail without proper risk management.
Key Elements:
a. Position Sizing
Never risk more than 1-2% of your account on a single trade.
b. Stop Losses
Always define your exit point before entering a trade to prevent major losses.
c. Take Profit
Predefined profit targets help lock in gains and avoid greed.
d. Risk-to-Reward Ratio
A minimum of 1:2 (risk $1 to gain $2) ensures long-term profitability.
e. Diversification
Avoid putting all your capital into one asset or trade type.
Good risk management is not optional—it’s essential to long-term survival and success.
12. How to Choose the Right Strategy
Every trader is different, so choosing the right strategy depends on your:
- Personality: Are you patient or impulsive?
- Time availability: Can you monitor markets during the day?
- Risk tolerance: How much volatility can you handle?
- Capital: Some strategies require more margin or investment
Start by demo trading different strategies, track your results, and adjust based on performance.
13. Backtesting and Journaling
Before going live with any strategy, it’s critical to backtest it using historical data. This helps verify its viability.
Once live, maintain a trading journal that records:
- Entry and exit points
- Strategy used
- Emotions felt during the trade
- Mistakes and lessons learned
Reviewing your journal periodically helps identify patterns in behavior and improve over time.
14. Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Overtrading: Taking too many trades leads to burnout and losses.
- Chasing the market: FOMO (Fear of Missing Out) results in bad entries.
- Ignoring the plan: Deviating from your strategy causes inconsistency.
- Revenge trading: Trying to win back losses quickly usually leads to more losses.
- No stop loss: A recipe for blowing up your account.
Discipline and consistency often matter more than the strategy itself.
Conclusion
Trading strategies are the backbone of a successful trading career. From day trading and scalping to swing and trend following, each strategy offers unique benefits and challenges. There’s no “one-size-fits-all”—what works for one trader may not suit another. The key is to experiment, analyze your results, and choose a strategy that aligns with your personality, goals, and risk profile.
Remember, the journey to profitable trading is a marathon, not a sprint. Master the strategies, manage your risks, and stay emotionally grounded. Over time, with discipline and persistence, success in the markets is achievable.